Renting an office is a responsible and strategic step for any business, regardless of its size. The choice of a suitable space affects the efficiency of the team, employee comfort, and the overall impression on clients. However, office rental is also one of the largest expense items that can significantly impact a company’s financial health.
Often, entrepreneurs, especially those renting an office for the first time, underestimate the importance of careful budget planning. Unexpected expenses, hidden fees, or poorly drafted lease agreements can lead to financial difficulties. In this article, we’ll discuss the main factors that determine office rental costs and provide tips to avoid unpleasant surprises.
Key Factors Affecting Office Rental Costs
Estimating an office rental budget requires understanding the aspects that influence the price. The main factors include:
Location of the Premises
The choice of area is one of the key factors determining rental costs. Prices in city centers are typically much higher than in suburban or outlying areas due to the convenience of infrastructure, the prestige of the location, and access to public transportation.
However, central locations aren’t always the optimal choice. For instance, companies that don’t work directly with clients may benefit from renting in quieter neighborhoods where prices are lower.
Office Space
The choice of space directly depends on the number of employees and the type of business. According to international standards, each employee requires 5–8 m² of workspace. For small teams (5–10 people), a compact office of 50–70 m² might suffice. However, if you plan to expand your staff, consider this when selecting a space.
In addition to workstations, think about areas for meetings, relaxation, document storage, or equipment. The calculation of space should be as accurate as possible, as excess square footage means additional expenses.
Type of Office Premises
The cost also depends on the office class:
- Class A – Modern business centers with all amenities, high levels of comfort, and prestige.
- Class B – Mid-level offices, often in renovated buildings with modern finishes.
- Class C – Budget options, typically in older buildings with minimal additional services.
For startups or small companies just starting out, Class B or C offices may be the most practical choice.
Lease Duration
The longer the lease term, the more favorable the conditions can be. Many landlords offer discounts for long-term agreements (one year or more). On the other hand, short-term leases, such as a few months, often come with higher rates due to the risk for landlords.
Additional Services and Costs
Rental agreements may include expenses for security, cleaning, utilities, internet access, or even equipment maintenance. These costs are rarely included in the base rent, so it’s essential to clarify them in advance.
How to Properly Estimate an Office Budget
Estimating an office rental budget involves a combination of analysis, research, and strategic planning. To avoid mistakes, follow a clear step-by-step strategy:
- Assess Your Company’s Needs
Before searching for an office, determine what you need. Answering the following questions will help narrow down your search:- How many employees will work in the office?
- Do you need meeting rooms or private offices?
- What infrastructure should be nearby (cafes, banks, transportation)?
- Compare Market Offers
Research the rental market in your city. Use listing websites, contact real estate agencies, and compare lease agreements. This will help you find the best price-to-quality ratio. - Include a Contingency Budget
Never allocate your entire budget solely for base rent. Set aside 10–15% of the total amount to cover unexpected expenses. - Review Lease Terms
Carefully read the lease agreement before signing. All terms regarding costs, duration, utility payments, and responsibilities should be clearly stated.
Hidden Costs of Office Rental
When renting an office, entrepreneurs often encounter expenses that aren’t immediately obvious. These include:
Renovation and Furnishing
Even if an office looks appealing at first glance, its condition may require additional investment. Cosmetic repairs, furnishing workspaces, and purchasing equipment are just some of the potential costs. If the space is "empty," you may also need to budget for lighting, blinds, air conditioners, decorative elements, or even plumbing work. These investments can make up a significant portion of the initial budget.
Utility Payments
Landlords often state only the base rent, leaving utilities as a separate cost. These may include electricity, heating, water, waste disposal, and other services. If the premises use centralized heating or air conditioning systems, these costs can be significantly higher than average. Also, check whether payments are fixed or consumption-based.
Parking
In city centers, parking can become a serious issue. The cost of a single parking spot in such areas is often substantial. If the lease doesn’t include free parking for employees or clients, finding alternatives could add financial strain.
Maintenance Fees
Beyond rent, there may be monthly fees for building maintenance. These could cover cleaning, security, elevator maintenance, or air conditioning systems. While some business centers include these costs in the overall rent, they’re often listed as separate charges.
Legal Fees
Having a lawyer review the lease agreement is a recommended step to avoid future issues. An experienced professional can identify hidden terms or potential risks. The cost of such services depends on the complexity of the agreement but is a worthwhile investment to protect your interests.
Contingency Reserve
In addition to primary expenses, always set aside a reserve for unforeseen circumstances. For instance, there may be additional costs for internet setup, adapting engineering networks, or installing a video surveillance system.
How to Avoid Unexpected Costs
A careful approach to analyzing the lease agreement and rental terms can help minimize financial risks. Here are the main recommendations:
- Thoroughly Analyze Lease Terms
The lease agreement is the primary document governing your relationship with the landlord. All costs should be clearly outlined, including rent, utilities, maintenance fees, and penalties for breaches. If any clauses are unclear, seek clarification before signing. - Work with Reliable Agencies
Partnering with professional real estate agencies can provide transparency and reduce risks. Check the reputation of the agency or landlord by reading online reviews. A reliable landlord will always provide the necessary documents and answer all your questions. - Negotiate Terms
Don’t hesitate to discuss terms directly with the landlord. Demonstrating interest in a long-term lease or willingness to take on minor responsibilities may earn you a discount or more favorable conditions. - Engage a Lawyer for Agreement Review
Even if the terms seem straightforward, have the agreement reviewed by a lawyer. A legal expert can identify hidden risks or pitfalls written in complex language. - Inspect the Premises Before Signing
Personally visit the office before signing the lease. Check the technical condition of the premises, the state of utilities, and the availability of necessary furniture or equipment. - Agree on Additional Services in Advance
Discuss all aspects that may impact costs, such as parking, security, cleaning, or internet. Clarify whether services can be modified or canceled if they’re no longer needed.
Example of Budget Estimation
Here’s a sample calculation for estimating the budget for a 50 m² office in Kyiv:
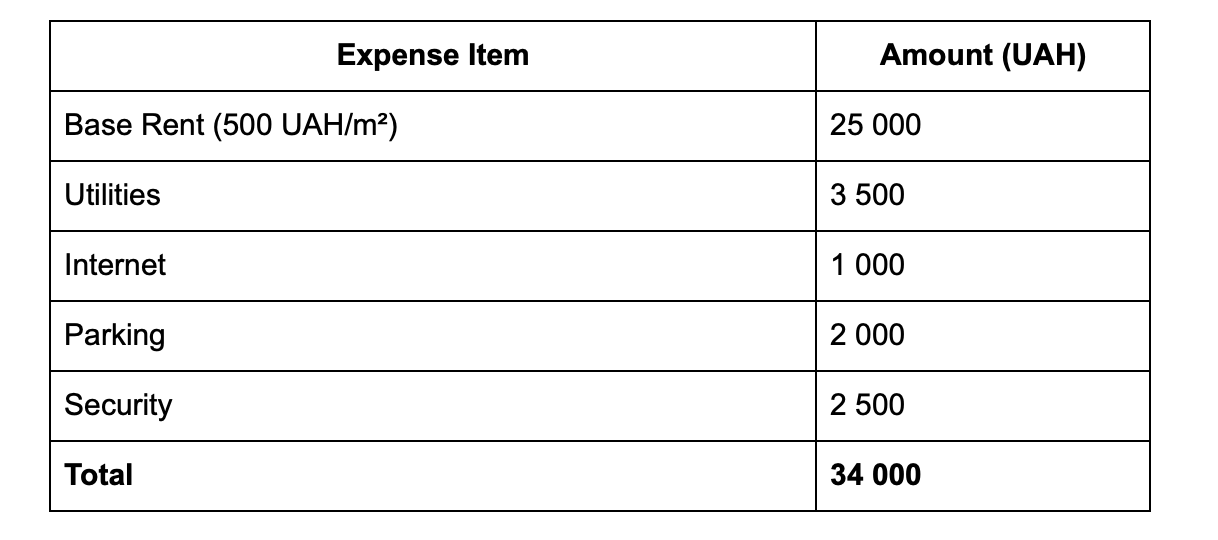
In this example, the total office costs amount to 34,000 UAH, but it’s crucial to set aside a 10–15% reserve for additional expenses.
Conclusion
Estimating an office rental budget is a critical step in business planning. Careful analysis, consideration of hidden costs, and a thoughtful approach to choosing premises can help avoid financial risks. Remember: an office is not just a workspace but also the face of your company, shaping the first impression for clients and partners.
